Seminar For Students On ‘Secrets of Rational Nutrition And Longevity’ at TSUULL University
There is a saying: ‘A healthy body means a healthy mind’. In fact, a physically healthy and strong person will be productive and effective in his work. The diet of students may not always be in order. But there are golden rules in eating that we should follow.
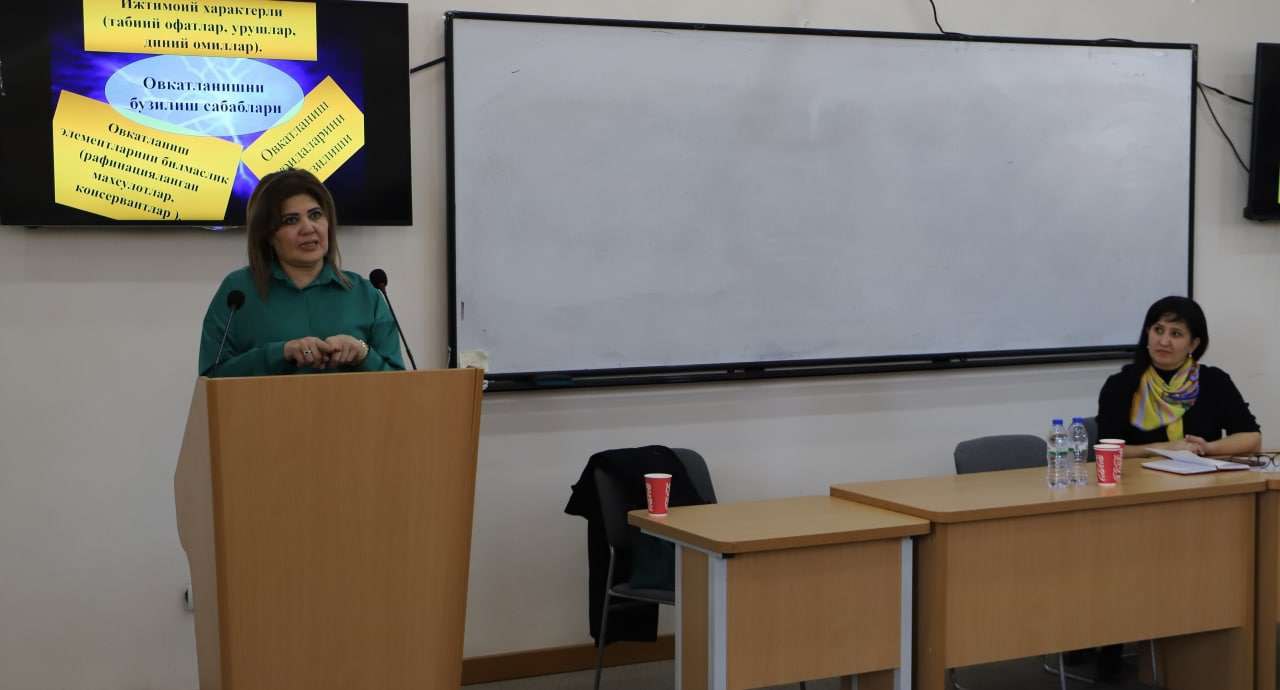
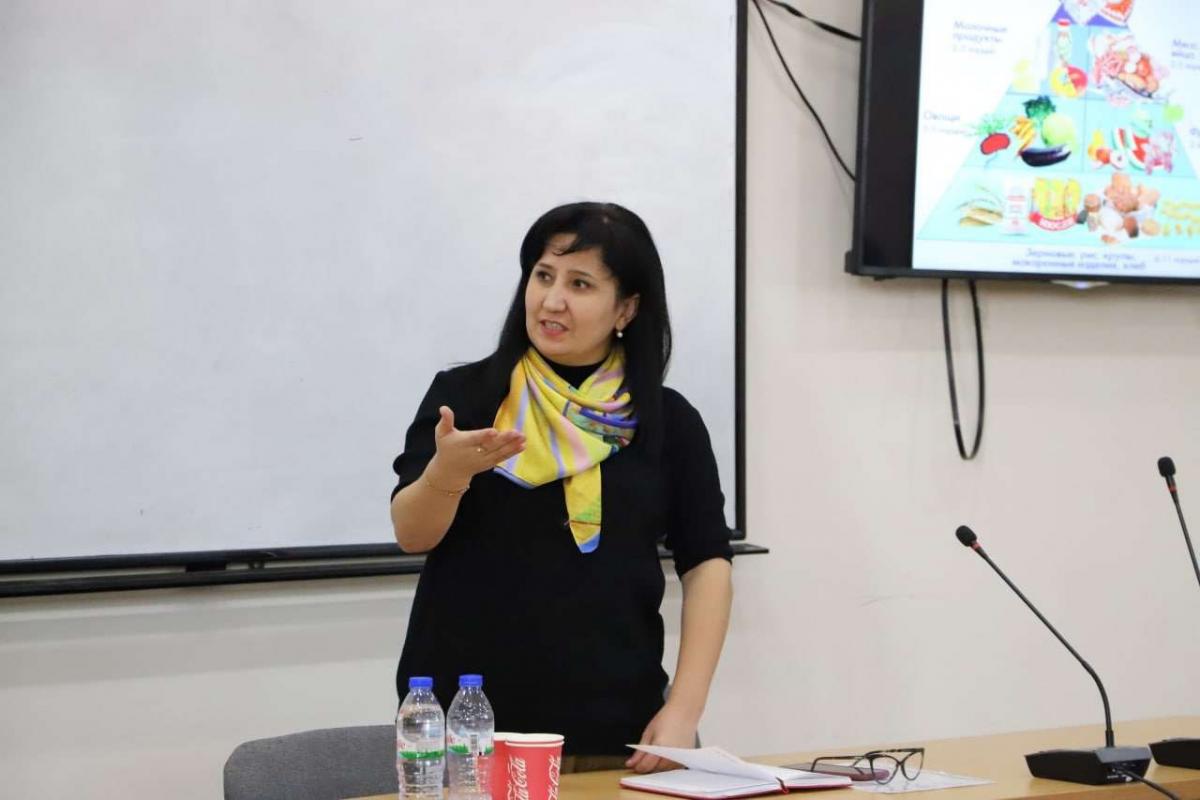
A Round-table Discussion was held for TSUULL Faculty of Translation Theory and Practice students and teachers on the topic ‘Secrets of Rational Nutrition and Longevity’. The guest of the panel discussion was Nilufar Rasulova, Associate Professor of the Tashkent Pediatric Medical Academy.

Credit: Healthy Eating Pyramid by Harvard School of Public Health
During the long-day meeting, participants discussed the phenomenon of healthy diet and the secrets of longevity. The aim was to emphasize the importance of a healthy diet and urge the students to pay attention to their menu by demonstrating the poor healthy diet situation in the global and local context. As well as to demonstrate the consequences of a lack of balanced food intake by showing reports by panelists.
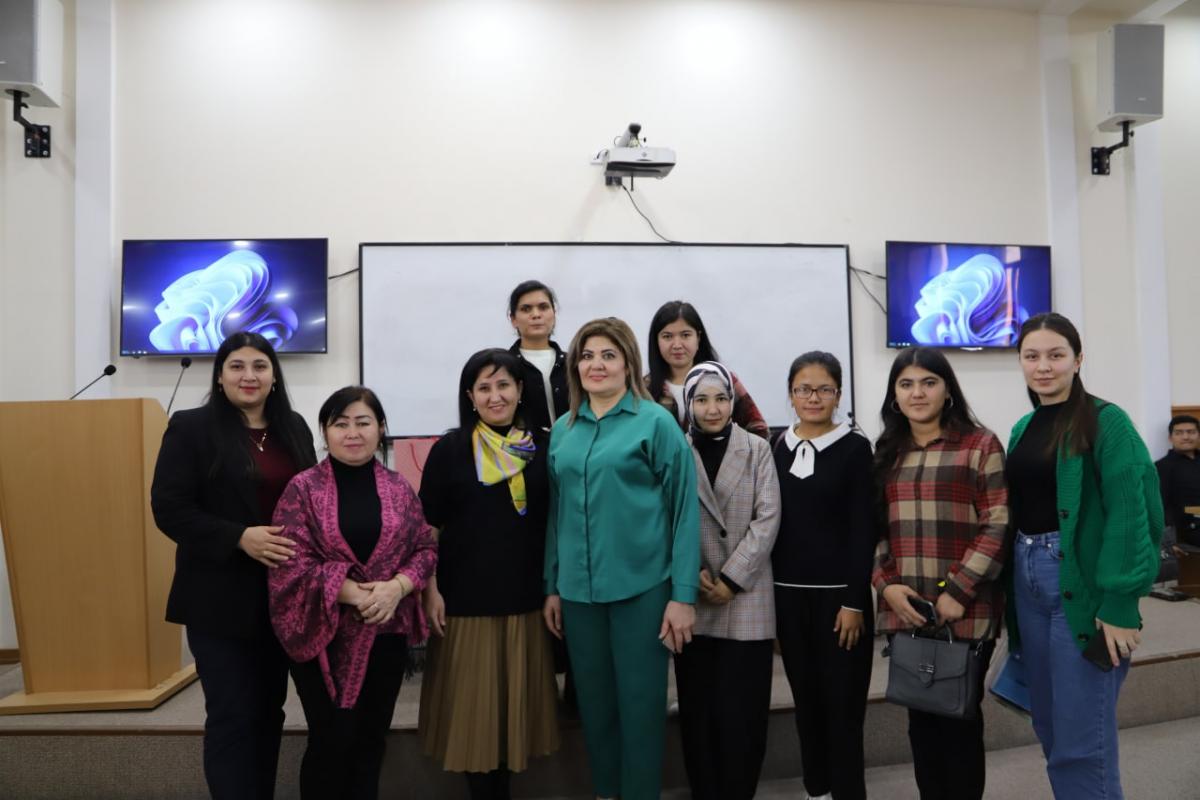

After demonstrating the current situation in the world and Central Asia for instance, the aim of the coming discussions is meant to educate the students on what is considered to be healthy food and unhealthy food, in order for them to make well-grounded decisions regarding their diets.

Thus we would like to share the Expert’s words bullet points of the discussion:
Point 1.
Eating healthy food is important
- At least 2.7 million people around the world die each year as a result of not getting enough fruits and vegetables in their diets, according to the World Health Organization.
- Eating a healthy diet instead of an unhealthy diet can help you get all the essential nutrients you need and limit your risk for a number of health conditions.
Point 2.
Healthy foods that are good for your body
- Healthy diets are made up mainly of nutrient-rich foods, such as legumes, fruits and vegetables, whole grains, low-fat dairy products, lean protein and nuts and seeds.
Point 3.
Unhealthy foods
- In comparison, unhealthy diets are high in fat, saturated fat, trans fat, sodium and added sugars. These diets often contain a lot of processed or fast foods that are high in calories but don't contain many nutrients.
- Poor nutrition can impair our daily health and well-being and reduce our ability to lead an enjoyable and active life. In the short term, poor nutrition can contribute to stress and tiredness, and over time, it can contribute to the risk of developing some illnesses and other health problems such as obesity, depression, acne and diabetes.
Point 4.
Calories and Energy balance
- Calories are units of energy that a food or drink provides. We need calories to give us enough energy to move around, stay warm, grow, work, think, and play. Even our blood circulation and digestion need the energy gained from calories in order to function well.
- It is important to maintain a balanced calorie intake. If we put more calories in than we use up (calorie surplus), those excess calories are stored as body fat. Continuing to put more calories in than we need, will lead to excess weight.
- Eating too few calories, or burning up more energy through physical activity than we are consuming, will lead to weight loss over a period of time (calorie deficit). However, it’s important to consume enough calories to have the energy your body needs for everyday activities, as well as to stay healthy.
Point 5.
1000 calories vs 1000 calories
- What is the difference between 1000 calories of healthy food, and 1000 calories of junk food? – Technically, 1000 calories of processed food contains precisely the same amount of raw energy as 1000 calories of healthy food.
- If you were to eat 1000 calories totally from processed food, you're likely to go through peaks and troughs with your energy and feel hungry for much of the day. Food could be dense with calories, but it doesn't mean it has the nutrients required to keep your energy levels high.
- The most significant difference between healthy food and junk food is the food volume – 1000 calories of healthy food will fill up potentially a few plates, whereas 1000 calories of junk food would look tiny in comparison. Further, because healthy food is likely to contain whole grains, healthy fats and protein, you're much more likely to be satiated, and you won’t feel hungry again soon after eating.
Point 6.
Combine Good Nutrition With Other Healthy Habits
- Mention the portion-controlled plate, ½ of vegetables, ¼ good pertain, ¼, various carbohydrate
- Exercise or move your body daily: Exercise has many benefits, not only for your physical health but also for your mental health. It can help you to feel better, even if you’re feeling okay. Reduce the risk of obesity and help you lose weight if you want to, which could be good for your health overall.
- Drink at least 1 liter of water daily: Water is a healthy alternative to sugar-sweetened beverages. Drinking water improves memory and attention, helps you to maintain a healthy weight, helps you fight acne and reduces the risk for some chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Staying hydrated helps stay alert and focused and may improve cognitive functioning.
- Get enough sleep: Teens need 8 to 10 hours of sleep each night. Getting enough sleep has many benefits. It can help you to think more clearly and do better in school, stay at a healthy weight and reduce stress and improve your mood.

Useful Sources:
The World Food Programme (WFP) is the food-assistance branch of the United Nations. It is the world's largest humanitarian organization focused on hunger and food security, and the largest provider of school meals.
Founded in 1961, it is headquartered in Rome and has offices in 80 countries. In addition to emergency food relief, WFP offers technical assistance and development aid, such as building capacity for emergency preparedness and response, managing supply chains and logistics, promoting social safety programs, and strengthening resilience against climate change. The agency is also a major provider of direct cash assistance and medical supplies and provides passenger services for humanitarian workers.