|
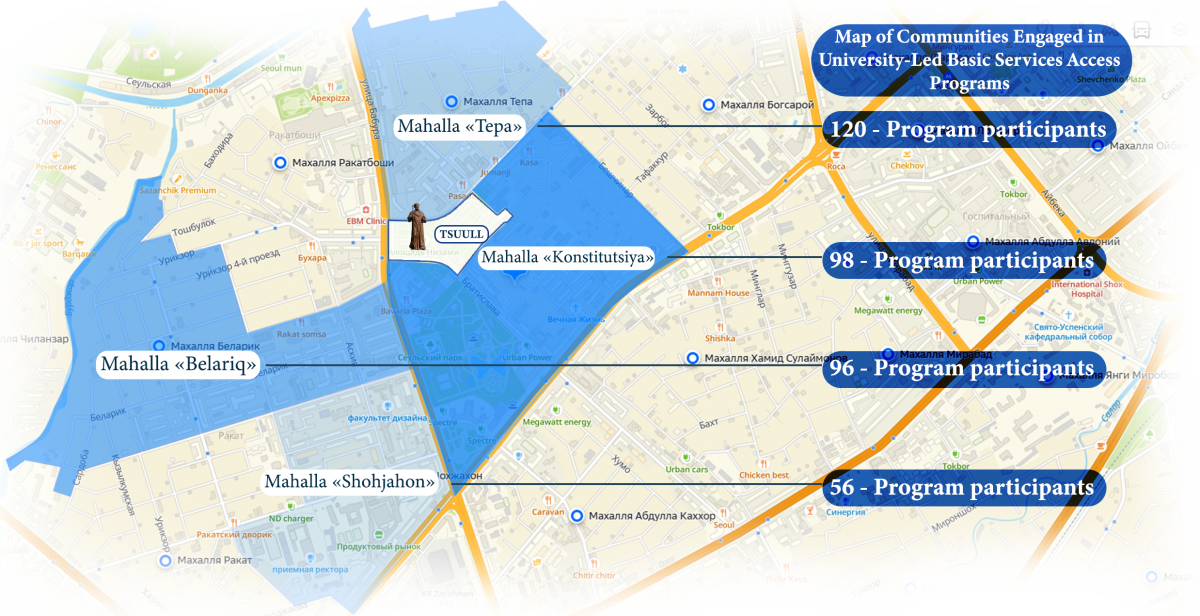
TSUULL’s Digital Skills and Literacy Programs aim to provide equitable access to essential technological competencies for community members, empowering them to participate confidently in an increasingly digital world. As a long-term, ongoing initiative, the program is specifically designed to reduce digital inequality and support vulnerable populations residing in neighborhoods surrounding the University. By focusing on youth, women, senior citizens, and low-income families, the program ensures that those most at risk of exclusion gain the skills needed for education, employment, and daily life. |
|
Digital Empowerment Pathfinders
with a special focus on women facing socio-economic hardship
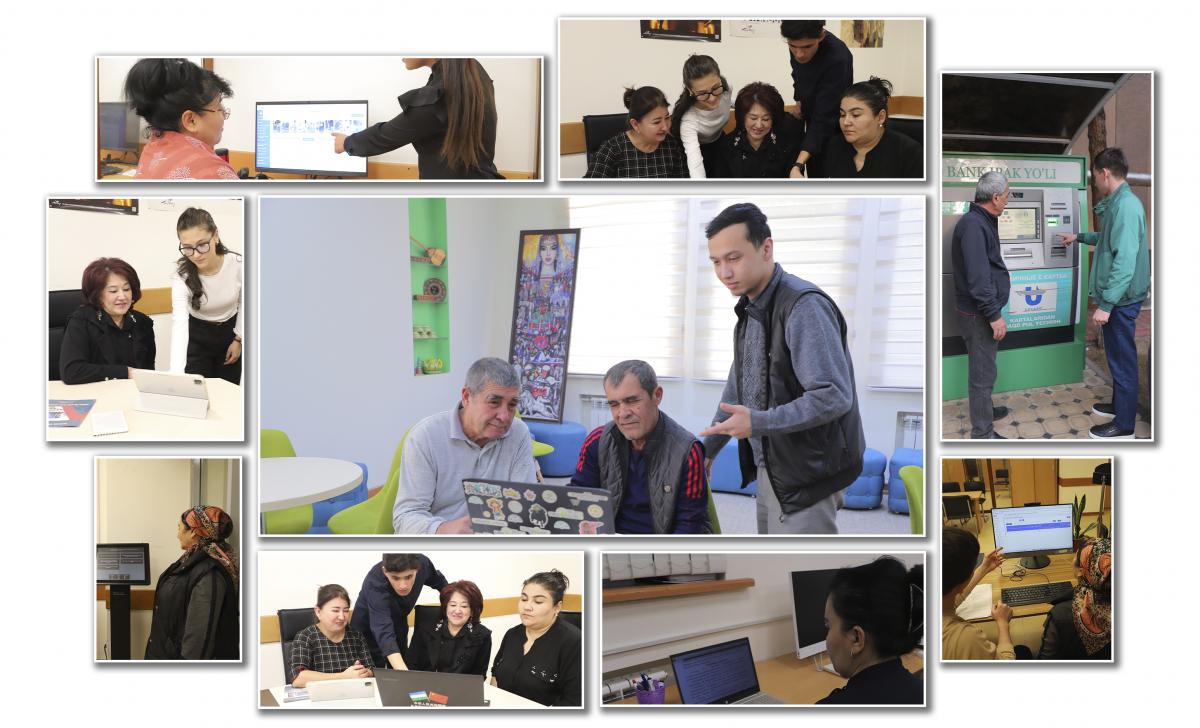

|
This group consisted predominantly of women who had long been excluded from educational, economic, and social opportunities. Many participants came from low-income or unstable family environments, including: How the Program Transformed Their LivesThe training program was intentionally designed to address these barriers and help participants rebuild confidence, acquire essential skills, and strengthen their economic independence.
Overall Impact: Independence, Confidence & Financial Stability |
|
Future-Ready Digital Achievers
with a special focus on youth facing socio-economic hardship
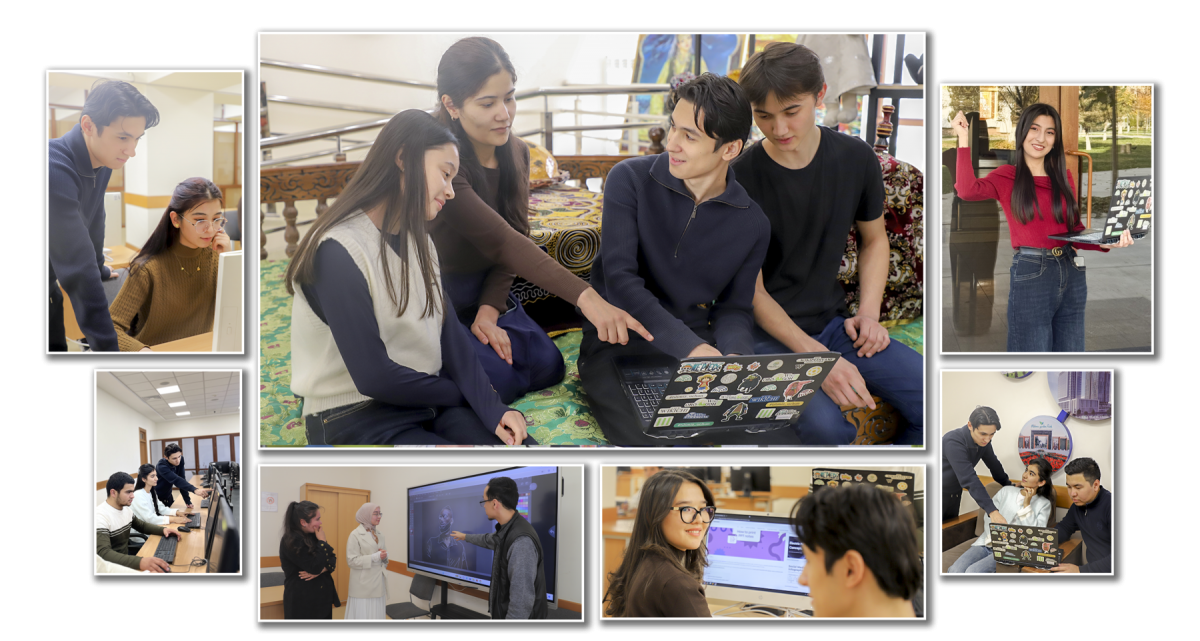

|
This training track was designed specifically for highly vulnerable youth |
|
Digital Confidence Builders
with a special focus on socially and economically vulnerable older adults

|
TSUULL’s Digital Skills and Literacy Program not only reduces the digital divide for senior community members but also provides structured support that enables them to participate in financially and socially sustainable initiatives. While older adults are not typically the primary group for business start-ups, the program equips them with foundational competencies that directly contribute to economic resilience, financial independence, and improved community participation. |



|
|
|